
Leveraging AI
AI is not a standalone topic in this course. It is the way you will apply nearly every part of The Consultant’s OS more effectively.
Starting in Week 2, you’ll learn how to use AI tools to accelerate your research, sharpen your analysis, and improve how you are able to communicate. The OS remains the foundation; AI simply increases your leverage.
Getting Leverage with AI
Think of AI as an amplifier for The Consultant’s OS:
| OS Capability | Without AI | With AI |
|---|---|---|
| Research | Hours of manual searching | Rapid synthesis across sources |
| Analysis | Slow iteration on models | Fast hypothesis testing |
| Communication | Multiple draft cycles | Accelerated refinement |
| Learning | Delayed feedback | Instant practice partner |
AI doesn’t replace judgment, structure, or rigor. It makes each of them faster, cheaper, and more scalable.
You’ll use two broad categories of AI tools in this course. Both rely on the same underlying language models. In principle, either could answer the same question.
The difference isn’t the underlying model but the tools wrapped around it. Web chatbots operate through a browser interface with limited, manual file uploads and limited agentic behavior. AI agents operate through you a code editor and terminal (CLI), with direct access to your file system, the ability to execute code, and the capacity to chain actions together. Same model but different capabilities.
This leads to an emerging discipline you’ll practice throughout the course: context engineering, which is deciding what information an AI system has access to when it responds.
- Prompt engineering focuses on how you ask: wording, structure, and tactics for framing a request.
- Context engineering focuses on what the AI knows: your files, your data, your project, and your constraints.
You can write a great prompt, but if the AI doesn’t have access to your data, your documents, or know about your project, it can only be so helpful. Context engineering is about optimizing what information and tools the AI model has access to in order to push it’s abilities far beyond what’s possible from a prompt in a web based chatbot.
Web Chatbots
Tools: Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini
Web-based chatbots are amazing, almost magical conversational interfaces. You type; the AI responds; you refine. They live in your browser and require no setup.
You can upload files to chatbots, but that context is manual and fragile. You decide what to upload, conversation by conversation. The AI sees only what you explicitly provide, cannot infer relationships across files, and forgets everything once the conversation ends.
Chatbots are ideal when the AI doesn’t need deep knowledge of your specific project. They shine in situations like:
- Research and synthesis — Understanding industries, companies, or unfamiliar concepts
- Structuring thinking — Building MECE frameworks, testing hypotheses, developing storylines
- Writing and editing — Drafting emails, refining prose, sharpening arguments
- Practice and preparation — Case interview drills, networking conversation prep
When you just need to think, explore, or communicate, chatbots are often the fastest option.
AI Agents:
Tools: Claude Code, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, OpenAI Codex, Cursor
AI agents use the same underlying models as web chatbots but they are accessed and operate primarily through a locally installed terminal or code editor such as VS Code, Antigravity, or Cursor.
That is, AI agents are accessed via tools that historically have been the domain of software developers and data scientists, in places where few consultants dared enter.
For most of computing history, these tools required specialized knowledge that tools years to develop. You had to understand syntax, commands, file systems, and obscure error messages. Those knowledge barriers kept them largely confined to developers.
That barrier is now gone.
Large language models are fundamentally text-in, text-out systems. They excel at reading text, generating text, and reasoning over text.
VS Code and the command line (terminal) are also fundamentally text-based:
- Source files are text
- Data files are often text
- Logs and errors are text
- Commands are text
This makes them the native habitat of LLMs.
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) were designed for humans. Because we are vision-dominant, windows, icons, and buttons made computers easier to use. Even the name Windows is a self-reference to this design choice. But what is intuitive for humans is often unnecessary for AI agents, which operate natively in text.
This has led to a “CLI renissance” where the command line is very much back in style and more powerful than ever before.
With AI agents assisting you, tools that once required years of training now allow you to describe what you want in plain English while the AI translates that intent into concrete actions.
This is the quiet revolution that so far few people have put words to or are fully appreciating: developer tools have become general-purpose thinking and execution tools for all knowledge workers.
Because agents operate inside your editor and terminal, they gain something chatbots cannot: full context.
They can:
- Read your project files
- Understand how documents and data relate
- Write new files and modify existing ones
- Run code, see errors, and fix them
- Chain multi-step workflows end to end
A useful mental model:
A web chatbot knows everything about the world but nothing about your project.
An AI agent knows everything about the world and can see exactly what you’re working on.
That difference matters enormously when you want to get the most out of AI models.
Chatbots vs AI Agents
| Criteria | Web Chatbot | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Response speed | Faster | Slightly slower (reads files first) |
| Setup required | None (just a browser) | Installation required |
| File context | Manual upload, limited | Automatic, full project access |
| Code execution | Limited (sandboxed Python) | Full (any language, your machine) |
| Output persists | No (copy-paste) | Yes (writes to files) |
| Best for | Thinking and drafting | Building and executing |
When to Use Each
| If you need to… | Web Chatbot | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Brainstorm ideas | ✓ | ✓ |
| Research a company | ✓ | ✓ |
| Structure an argument | ✓ | ✓ |
| Practice a case interview | ✓ | |
| Analyze your dataset | ✓ | |
| Build a model from your data | ✓ | |
| Create files or deliverables | ✓ | |
| Automate a repetitive task | ✓ |
Rule of thumb: if the AI needs to take action, use an agent. Otherwise, use whatever is fastest.
What counts as “action”? Anything beyond generating text:
- Reading your files — analyzing datasets, reviewing documents, understanding your project
- Writing files — creating deliverables, saving outputs, building persistent artifacts
- Running code — executing scripts, testing solutions, iterating on errors
- Searching your system — finding files, grepping through codebases, locating specific content
- Executing commands — installing packages, running builds, interacting with APIs
- Chaining operations — multi-step workflows where each step depends on the last
If your task involves any of these, reach for an agent. If you just need to think through a problem or get information, a chatbot in your browser is faster and simpler.
Setting Up Your AI Workflow
The Tools
VS Code is the open-source code editor (often called an IDE for Integrated Development Environment) that serves as the foundation for many AI coding tools. Both Cursor and Antigravity are built on top of VS Code, adding AI capabilities while preserving the familiar interface. If you learn one, you can use the others.
Recommended setup for this course:
- Antigravity (Google) — Our primary tool due to its generous free tier
- Claude Code — Recommended for students who want the most capable agentic coding experience ($20/mo). You can access Claude Code from any of VS Code, Antigravity, or Cursor, all of which have a very simliar look and feel. If you know one, you know them all.
AI Coding Agents Comparison
| Company | Product | Student Cost | CLI | VS Code Extension | Dedicated IDE | Web |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropic | Claude Code | $20/mo | ✓ | ✓ | claude.ai/code | |
| Gemini | Free Tier | ✓ | ✓ | Antigravity | aistudio.google.com | |
| Microsoft | GitHub Copilot | Free Tier | ✓ | ✓ | VS Code | github.com/copilot |
| OpenAI | Codex | $20/mo | ✓ | ✓ | chatgpt.com/codex | |
| Cursor | Cursor | Free Tier | ✓ | Cursor | cursor.com/agents |
Step 1: Install Software
Download and install the following IDEs on your laptop. Overtime you will tend to use only one but good to have exposure to all of them.
Step 2: Configure Your Environment
Troubleshooting tip: If at any point you get stuck or something is not working as expected, take a screenshot or copy/paste the command you ran plus error text into ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini and ask for help troubleshooting.
Mac
Open VS Code and launch a new terminal (Terminal → New Terminal). The terminal should appear as a new window pane within VS Code.
Copy/paste the following into the terminal and hit enter
# Download and install nvm:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bash
# in lieu of restarting the shell
\. "$HOME/.nvm/nvm.sh"
# Download and install Node.js:
nvm install 24
# Verify the Node.js version:
node -v # Should print "v24.13.0".
# Verify npm version:
npm -v # Should print "11.6.2".Once complete you are ready to install the AI agents by running the following commands in the terminal.
Claude Code:
curl -fsSL https://claude.ai/install.sh | bashAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent. (requires a paid Claude account, $20 per month)
claude
Google Gemini CLI:
npm install -g @google/gemini-cliAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
gemini
GitHub Copilot:
npm install -g @github/copilot
copilotAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
copilot
OpenAI Codex:
npm install -g @openai/codex
codexAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
codex
Windows
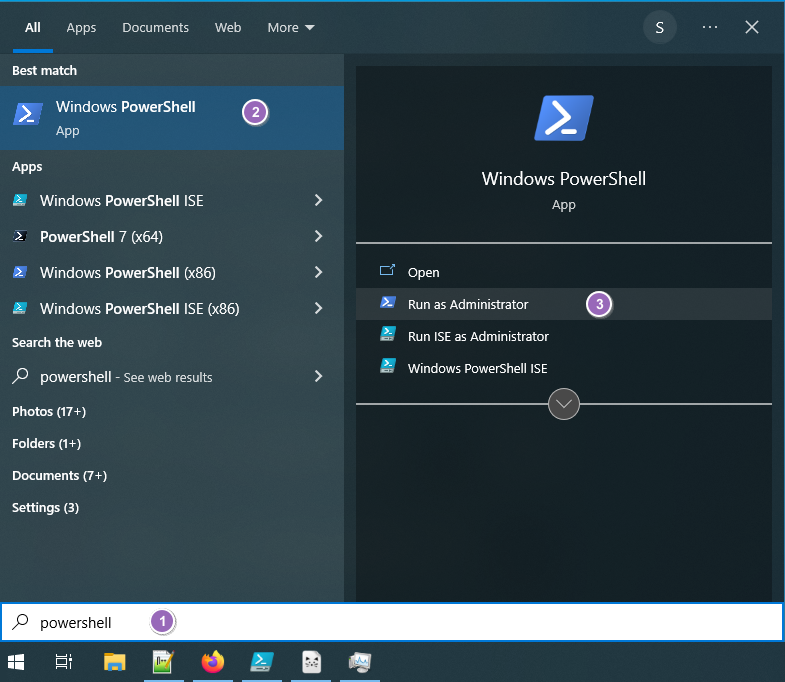
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- Press Start
- Type PowerShell
- Right-click Windows PowerShell
- Select Run as administrator
Copy/paste the following into PowerShell and hit enter:
# Download and install fnm (Fast Node Manager):
winget install Schniz.fnmClose and reopen PowerShell (as Administrator), then run:
# Download and install Node.js:
fnm install 24
# Verify the Node.js version:
node -v
# Verify npm version:
npm -vOnce complete you are ready to install the AI agents by running the following commands in the terminal.
Claude Code:
irm https://claude.ai/install.ps1 | iexAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent. (requires a paid Claude account, $20 per month)
claudeGoogle Gemini CLI:
npm install -g @google/gemini-cliAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
geminiGitHub Copilot:
npm install -g @github/copilotAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
copilotOpenAI Codex:
npm install -g @openai/codexAfter installation, run the following command in the terminal to activate the agent.
codexStep 3: Practice the Basics
Try these starter exercises:
- Research synthesis: “What are the key trends affecting [your target company’s] industry?”
- Structure building: “Help me create a MECE issue tree for [problem]”
- Case practice: “Give me a market sizing question and walk through it with me”
Supports: Networking Tracker
Use AI to prepare for networking conversations by researching the person and firm before you reach out.
Help me prepare for a networking conversation with a consultant:
**Person I'm Meeting**
- Name: [NAME]
- Firm: [FIRM NAME]
- Role: [TITLE]
- LinkedIn profile: [URL or key details]
**Prep Questions**
1. What does this person's career path tell me about what they value?
2. What are 3 thoughtful questions I could ask that show I've done my homework?
3. What aspects of my background might resonate with their experience?
4. What's happening at their firm right now that I should know about?
**Conversation Goals**
Help me identify:
- 1-2 specific things I want to learn from this conversation
- How I can be helpful or interesting to them (not just ask for things)
- A natural way to follow up after the conversationSupports: P1 Intelligence Brief
Learn to use AI to analyze financial filings and extract key insights from your target company’s 10-K.
Help me analyze the 10-K filing for [COMPANY NAME]:
**Company Overview**
1. What does the company describe as its core business?
2. What are the key segments and what % of revenue does each represent?
3. What does management highlight as key competitive advantages?
**Financial Analysis**
4. What are the 3-year trends in revenue, gross margin, and operating margin?
5. What are the largest expense categories and how are they trending?
6. What does the cash flow statement tell us about the business model?
**Risk Factors**
7. What risks does management highlight as most significant?
8. Are there any risks that seem understated or missing?
**Management Discussion**
9. What is management's narrative about the company's performance?
10. What strategic priorities do they emphasize for the coming year?
Summarize the key takeaways in 3-5 bullet points.AI-Assisted Consulting Actions
Think Clearly with AI
| Core Action | How AI Helps |
|---|---|
| Diagnose current state | Synthesize news, filings, analyst reports quickly |
| Define the problem | Pressure-test your problem statement for clarity |
| Build MECE structures | Generate and critique issue trees |
Get to the Right Answer with AI
| Core Action | How AI Helps |
|---|---|
| Build fact base | Research companies, industries, competitors rapidly |
| Estimate and bound | Sanity-check assumptions, find benchmarks |
| Synthesize | Draft “so what” statements, identify patterns |
Move Work Forward with AI
| Core Action | How AI Helps |
|---|---|
| Workplanning | Draft project plans, identify dependencies |
| Progress without certainty | Explore multiple scenarios quickly |
Create Impact with AI
| Core Action | How AI Helps |
|---|---|
| Craft storylines | Structure Pyramid Principle arguments |
| Communicate with brevity | Edit for conciseness, strengthen logic |
| Prepare for stakeholders | Anticipate questions, practice responses |
Supports: Networking Tracker
Use AI to build a comprehensive research profile on your target firms, going deeper than surface-level information.
Help me build a detailed research profile for [FIRM NAME]:
**Firm Deep Dive**
1. What is their official value proposition and how do they differentiate from competitors?
2. What are their key practice areas and industry focuses?
3. What notable projects or client work have they publicized recently?
4. Who are their key leaders and what backgrounds do they have?
**Culture and People**
5. What do Glassdoor/Fishbowl reviews say about the culture (patterns, not outliers)?
6. What do LinkedIn profiles of recent hires tell us about who they value?
7. What do current employees post about on LinkedIn?
**Recruiting Intelligence**
8. When do they typically recruit? What's their timeline?
9. What's their interview process? How many rounds?
10. What types of cases do they tend to give?
**My Fit Assessment**
Based on all this research:
- Where am I a strong fit?
- Where do I have gaps to address?
- What should I emphasize in conversations with this firm?
Compile into a 2-page firm profile I can reference.Supports: P1 Intelligence Brief
Use AI to create a reusable template for analyzing companies throughout your project.
Help me create a structured analysis template for [COMPANY NAME] that I can use throughout the semester:
**Company Profile Template**
Create sections for:
1. **Company Overview**
- Business description
- Key products/services
- Geographic footprint
- Ownership structure
2. **Financial Summary**
- Revenue and growth trends (5-year)
- Profitability metrics
- Key financial ratios
- Capital structure
3. **Strategic Position**
- Market position and share
- Key competitors
- Competitive advantages
- Strategic challenges
4. **Industry Context**
- Market size and growth
- Key trends
- Regulatory environment
- Disruption risks
5. **Management and Governance**
- Key executives
- Recent strategic decisions
- Stated priorities
6. **Investment Thesis / Key Questions**
- Bull case
- Bear case
- Key uncertainties to resolve
Make this a template I can populate and update as I gather more information.AI Ethics and Professional Standards
What’s Acceptable
- Using AI to accelerate research you would do anyway
- Getting feedback on your writing and logic
- Practicing cases with AI as a partner
- Generating first drafts that you then refine
What’s Not Acceptable
- Submitting AI-generated work as entirely your own without disclosure
- Using AI during actual interviews (unless explicitly permitted)
- Relying on AI without developing your own judgment
The 80/20 Rule
AI can get you 80% of the way quickly. The last 20%, including judgment, nuance, and client context, is where you add value. Never outsource your thinking entirely.
Getting Started This Week
By the end of Week 2, you should be able to:
- Access Claude Code or Gemini within VS Code, Anitgravity, or Cursor
- Use an AI agent to help you conduct research and save the output to a markdown file for future reference.
Come to class ready to demonstrate your setup.